Understanding the Professionals Behind Your Ultrasound Exam
When patients schedule an ultrasound, they often interact with multiple medical professionals — each playing a critical role in producing accurate diagnostic results. Understanding the difference between a sonographer and a radiologist builds trust, clarity, and confidence in the imaging process.
At ProCare.com, our imaging workflows are designed to ensure every scan meets clinical quality standards and delivers reliable diagnostic insight.
If you’re new to ultrasound imaging, start with our complete overview:
👉 Ultrasound Services Near Me
What Is a Sonographer?
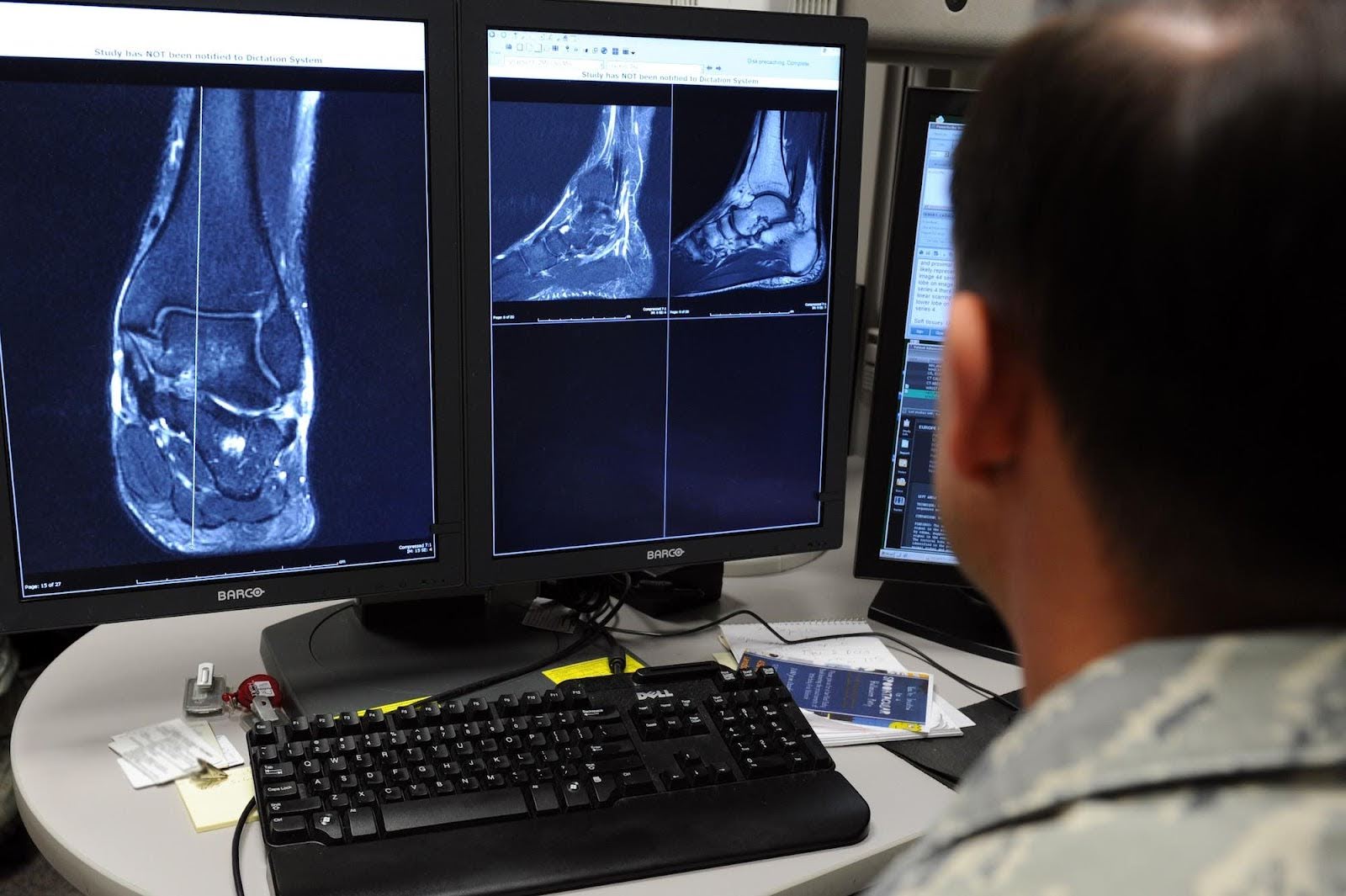
A sonographer (also known as an ultrasound technologist) is the healthcare professional who performs the ultrasound exam. They are responsible for operating the imaging equipment, positioning patients, capturing high-quality images, and ensuring patient safety and comfort.
Key Responsibilities of a Sonographer
- Prepare patients for imaging
- Position transducer for optimal visualization
- Adjust imaging parameters for clarity
- Capture diagnostic-quality images
- Identify anatomical landmarks
- Document findings for physician review
- Maintain equipment hygiene and calibration
Sonographers must understand anatomy, pathology, physics of sound waves, and patient care.
Training and Certification
Most sonographers complete:
- Accredited ultrasound education programs
- Clinical training hours
- National certification exams (ARDMS or equivalent)
- Continuing education
Their expertise ensures image accuracy before interpretation occurs.
What Is a Radiologist?
A radiologist is a medical doctor who specializes in interpreting medical images and generating diagnostic reports. Radiologists analyze ultrasound images to identify abnormalities, confirm diagnoses, and guide treatment decisions.
Key Responsibilities of a Radiologist
- Review ultrasound images
- Interpret findings
- Correlate imaging with clinical history
- Generate formal diagnostic reports
- Communicate results to referring providers
- Recommend follow-up imaging or treatment
Radiologists complete medical school, residency training, and board certification in medical imaging.
How Sonographers and Radiologists Work Together
The imaging workflow is collaborative:
- The sonographer performs the scan and captures high-quality images.
- Images are transmitted to the interpreting physician.
- The radiologist analyzes findings and produces a report.
- Your referring provider reviews results and discusses next steps.
This layered quality control ensures accuracy and accountability.
Why Professional Roles Matter for Image Quality
High-quality imaging depends on:
- Proper image acquisition
- Accurate interpretation
- Consistent quality standards
- Equipment calibration
- Ongoing education
Facilities that prioritize professional credentialing and imaging protocols deliver more reliable results.
This directly impacts exams such as KUB ultrasound where precise measurements and detection accuracy are critical.
Advanced Imaging and Specialized Training
Advanced imaging technologies such as 3D, 4D & 5D HD Live ultrasound require additional training and expertise to ensure optimal rendering, patient safety, and image interpretation.
Private Imaging vs Hospital Imaging Standards
Both private imaging centers and hospitals follow regulatory standards; however, workflow efficiency and patient experience may differ.
Our comparison guide on Private Ultrasound vs Hospital Imaging explains differences in scheduling speed, cost, accessibility, and care experience.
What Patients Should Look for in an Imaging Provider
Patients should verify:
- Credentialed sonographers
- Interpreting physician credentials
- Accreditation
- Equipment maintenance protocols
- Transparent reporting timelines
For a step-by-step provider checklist, see our guide on How to Find the Best Ultrasound Near You.
Why Patients Trust ProCare.com
✔ Certified imaging professionals
✔ Quality-controlled workflows
✔ Modern imaging systems
✔ Transparent reporting
✔ Patient-first care